Dynamic changes of histone methylation in male germ cells during Biology Diagrams Histone modifications also regulate cell cycle progression by marking specific chromatic regions. While many reviews have covered histone phosphorylation and acetylation as regulators of the cell cycle, little attention has been paid to the roles of histone methylation in the faithful progression of mitosis. In contrast to the mitosis-specific increase in phosphorylation, fewer changes are observed for other histone PTMs. Although histone methylation is more stable over the cell cycle and less affected by mitosis , some methylation marks such as H3K9me2/3, H3K79me2 and H4K20me1 increase during mitosis and are important for chromosomal stability [45

Our study focuses on the role of histone acetylation and H3 (Lys-4) methylation in the maintenance of the competency of these active genes during mitosis. To this end we have analyzed histone modifications across the promoters and coding regions of constitutively active, inducible, and inactive genes in mitotic arrested cells. The effect of histone methylation can differ depending on the position of the methylated residue and its level (mono-, di-, or trimethylated) [6,7]. Histone phosphorylation is an important mark for the DNA damage response (DDR). In this review, we focus on the role of histone PTMs in mitosis, from chromosome condensation to the regulation Histones can be mono-, di-, or trimethylated (me1, me2, me3) on lysines and mono-, symmetrically, or asymmetrically dimethylated on arginines. In general, histone methylation changes much less dramatically than phosphorylation during mitosis. H3K4me2 and H3K4me3 are typically associated with the 5′ ends of poised or active genes [7].

Translational Modifications in the Formation ... Biology Diagrams
Consistent with this, numerous proteins that read the histone methylation status at H3K4, H3K9, and H3K27 appear to be substantially displaced from chromosomes in mitosis 19,20,43,44,45,46.
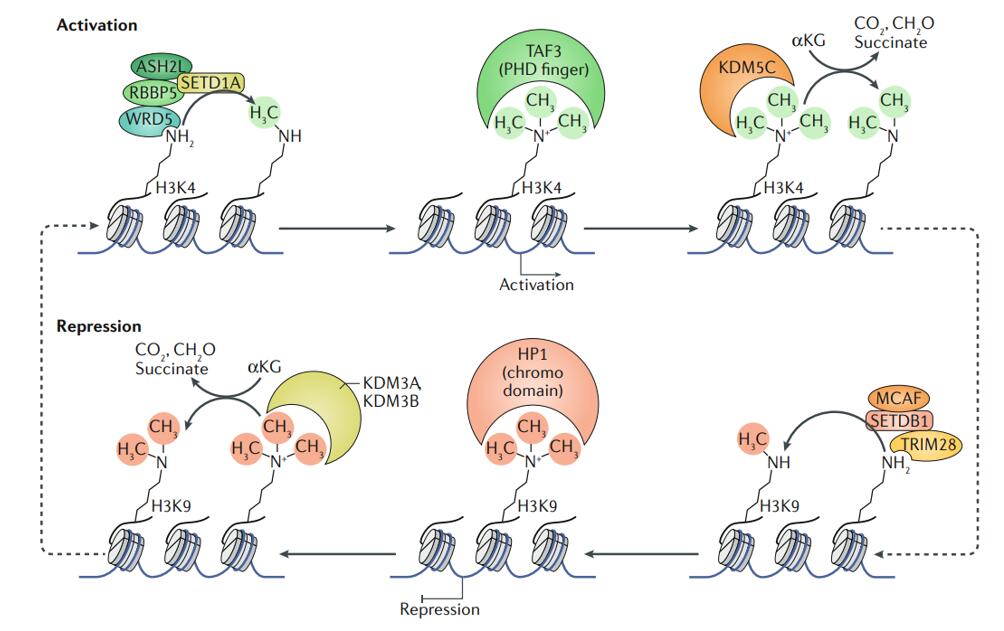
Histone methylation mainly occurs on the side chains of lysines and arginines. phosphorylation of H3S10 during mitosis occurs genome-wide and is associated with chromatin becoming more It is well known that histone codes can be involved in cell mitosis, 24, 25, 26 DNA damage and repair, 27, 28, 29 cell differentiation, 30 X chromatin inactivation, 31 and mediate transcriptional activation or inhibition, 32, Histone methylation was once considered irreversible until the discovery of LSD1 confirmed the existence of HDM The role of histone methylation during the cell cycle is still unclear (Wang and Higgins 2013; Xu et al. 2009).Numerous reports have shown that histone lysine methyltransferase (KMT) and demethylase (KDM) participate in mitotic progression (Table 1) (Black et al. 2012; Dimitrova et al. 2015).However, unlike histone acetylation, which is much lower at mitosis than at interphase (Kruhlak et al

Priming chromatin for segregation: functional roles of mitotic histone ... Biology Diagrams
Histone Acetylation and H3 (Lys-4) Methylation at Active and Inducible Genes during Mitosis—It is possible that the maintenance of acetylation and methylation at active promoters serves to signal the reassembly of transcriptional machinery at the G 1 or S phase; in such a case the promoter histone posttranslational modifications could play a
