FOOD CHAINS AND WEBS What is a Food Biology Diagrams As shown in the infographic below, a basic food chain is composed of producers, consumers, and decomposers. The 4 levels of the food chain consist of: PRODUCERS: At the bottom of the food chain, plants are natural producers and provide food and nutrients to consumers. For example, rabbits, cows, sheep, giraffes, elephants, caterpillars,

Organisms in the food chain are divided into trophic levels or feeding levels. The four essential parts are the sun, primary producers, consumers, and decomposers. Every food chain originates with the sun providing light and energy for plants to grow and ends with the decomposition of the animals. The decomposers such as fungi, and different types of insects are at the base of the detritus food chain. These decomposers help in the breaking of complex organic molecules into simpler substances, Now let's have a four-step grassland food chain example. In a grassland ecosystem grass is eaten up by insects; these insects are eaten by Some decomposers are specialized and break down only a certain kind of dead organism. Others are generalists that feed on lots of different materials. Thanks to decomposers, nutrients get added back to the soil or water, so the producers can use them to grow and reproduce. Most decomposers are microscopic organisms, including protozoa and bacteria.
Decomposer Definition and Examples Biology Diagrams
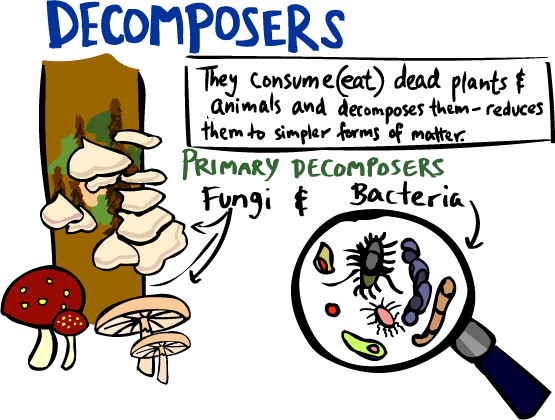
Though decomposer occupies the lowermost position in the food web, they are the most critical component of the food web. To understand how decomposers interact in their ecosystem in terms of the food chain and food web, refer to Figure 1 and the video below. Figure 1: Representative illustrations of the food chain components (and the energy flow). Check out examples of decomposers to see what they do. Dictionary Thesaurus Sentences Grammar Vocabulary Usage Reading & Writing Decomposers play an important role in food chains and are considered biotic factors in natural ecosystems. Explore examples of decomposers in different ecosystems to better understand what these organisms look and Food chain. In order to function, the entire food web relies on decomposers doing their job and returning those nutrients back into the cycle. Which lets the producers grow and feed the consumers. So yeah, decomposers are quite important to an ecosystem. Types of decomposers with examples 1. Fungi

The decomposers ensure that the food chain or food web will have an efficient energy cycle that will cover all the bases and stages of the whole thing. Without the decomposers, the soil where the plants and trees grow will have insufficient nutrients, which will inhibit the growth of all the plants in the whole biosphere . 4. Compared to other food chains, decomposer food chains always have a flow of energy. The decomposer food chain has a constant flow of food energy. 5. There are some decomposers in the decomposer's food chain that break down the remains of dead plants and animals and return their nutrients to the environment. In this way, decomposers play an Examples of detritivores are insects (such as mites, butterflies, mites), flies, crabs, millipedes, woodlice, earthworms, etc. Scavenger. Scavengers and decomposers are an important part of the food chain involved in an ecosystem for recycling nutrients and organic matter. Scavengers are known as the initiator of the decomposition process.
