Grazing Food Chain Biology Diagrams The Black-footed ferret population fell drastically in the earlier half of the 20th century, mainly due to habitat loss. Currently, habitat loss and introduced diseases are key threats to this species. The ferrets are entirely dependent on prairie colonies for shelter, food, and raising young.
Ferret and foxes are both carnivores 5. Apply: Now complete the Prairie Ecosystem food chain. Arrows point toward the animal that is eating. For example, would mean that the mouse is eaten the hawk. grass Prairie dog ferret foxes Reproduction for educational use only. Learn about food chains, producers, consumers, and population equilibrium. in an area, plus the natural landscape. A prairie is flat or gently rolling grassland with few trees, such as in parts of central United States and Canada. Once common, the black-footed ferret is an endangered animal. In 1986 there were only 18 black-footed 7) In Applying your Knowledge question 2 students are asked to build food chains using species cards for grassland organisms prepared in lessons 4.1. As students create food chains monitor that they begin the chain with a producer, and that animals are in an order that makes sense (herbivores are eating plants, carnivores are eating animals, etc.).

Student Exploration: Prairie Ecosystem ... Biology Diagrams
This ferret is carnivorous, and its main delicacy, which accounts for 90% of its diet, is the prairie dogs. Their throats, muzzle, and foreheads are white. The black-footed ferrets can be found inhabiting the grassland prairies. How do Ferrets Hunt? thus preventing their overpopulation in the food chain. It is vital to note that In a grassland food chain, the grass is the producer. It produces food using the sun's energy. The primary consumers follow the producers. Insects like grasshoppers are primary grasslands consumers as they depend on the green plant for their food (herbivores). Occasionally, primary consumers are omnivores as well, such as aardvarks. The black-footed ferret, scientifically known as Mustela nigripes, is a fascinating and endangered animal inhabiting the North American continent. Food Chain Dynamics: Black-footed ferrets are an essential link in the grassland food chain. They serve as prey for larger predators like raptors and coyotes. By sustaining populations of black

footed ferret, ferruginous hawk). Each survives by eating grassland plants, grassland animals, or In the food chain for a prairie grassland meadow the June grass is the producer, while the locust (herbivore) and the burrowing owl (carnivore) are the consumers. The arrows show the energy Understanding the Ferret's Ecosystem: A Deep Dive. The ferret's ecosystem is primarily defined by the temperate grasslands, specifically the North American Great Plains, where these fascinating creatures once thrived.It's an environment characterized by open, grassy landscapes dominated by prairie grasses and a network of burrows. These burrows, often initially dug by prairie dogs, are a

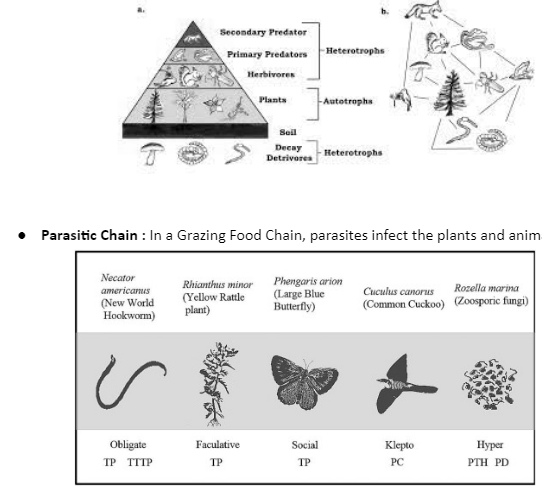
Grassland Food Chain Biology Diagrams
A food web is a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains. The arrows in the food web (to the right) point to the animal that gets energy by consuming it. For example, a black-footed ferret gets energy by eating prairie dogs and mice. And coyotes and foxes get energy from eating a black-footed ferret.