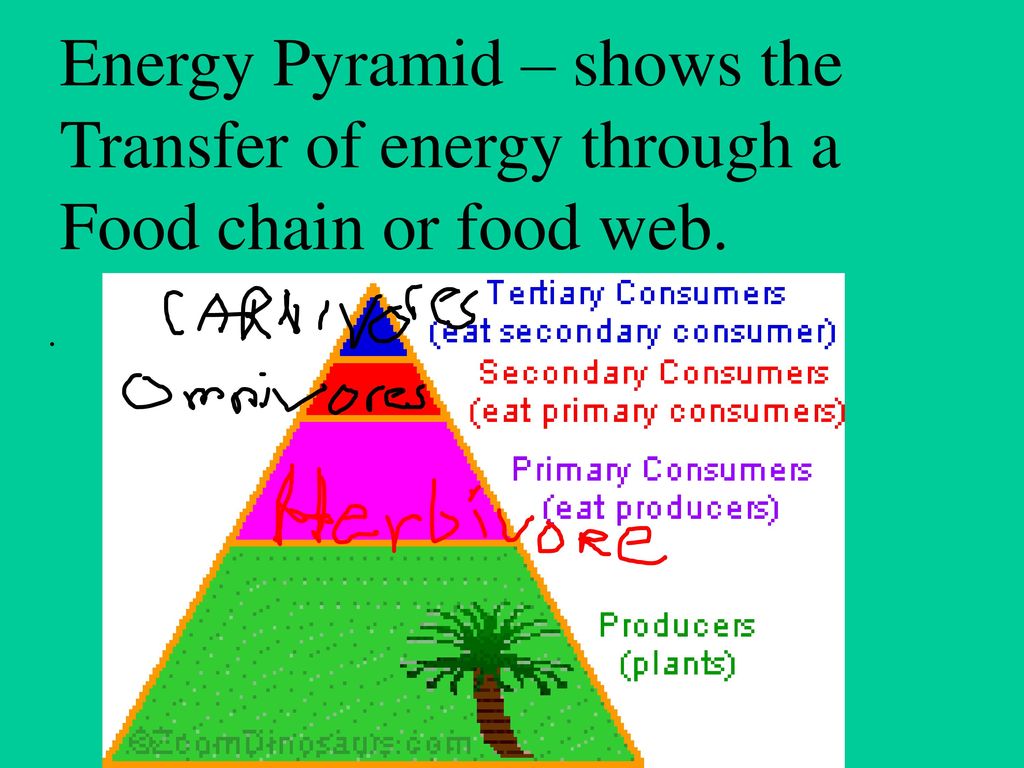
ppt download Biology Diagrams Several factors can influence energy transfer and efficiency in the ecological energy pyramid, including food chain length, predator-prey relationships, and ecosystem complexity. The length of the food chain can affect energy transfer, as longer chains tend to have lower energy transfer efficiencies. Predator-prey relationships can also impact
Every organism on Earth needs energy to live. Except for newly discovered species living in the deepest parts of the ocean, every species on Earth gets the energy they need to live from the sun. Ecosystem food chains and food webs can both be used to show how energy moves from the sun to different animals. Food ChainsAn ecosystem food chain shows the path of energy through a chain of different An energy pyramid, also known as an ecological pyramid or trophic pyramid, is a graphical way of representing energy flow at each trophic level within an ecosystem. It is similar to a food chain and establishes the predator-prey relationship.. The order of the bars representing each trophic level is based on which predator feeds on which prey. An important abiotic factor within an community is energy. Energy is transferred when one organism is eaten by another organism. A food chain is an easy way to diagram the flow of energy in a community. Click on the picture to watch the video to learn about food chains. The video will open in a new window.

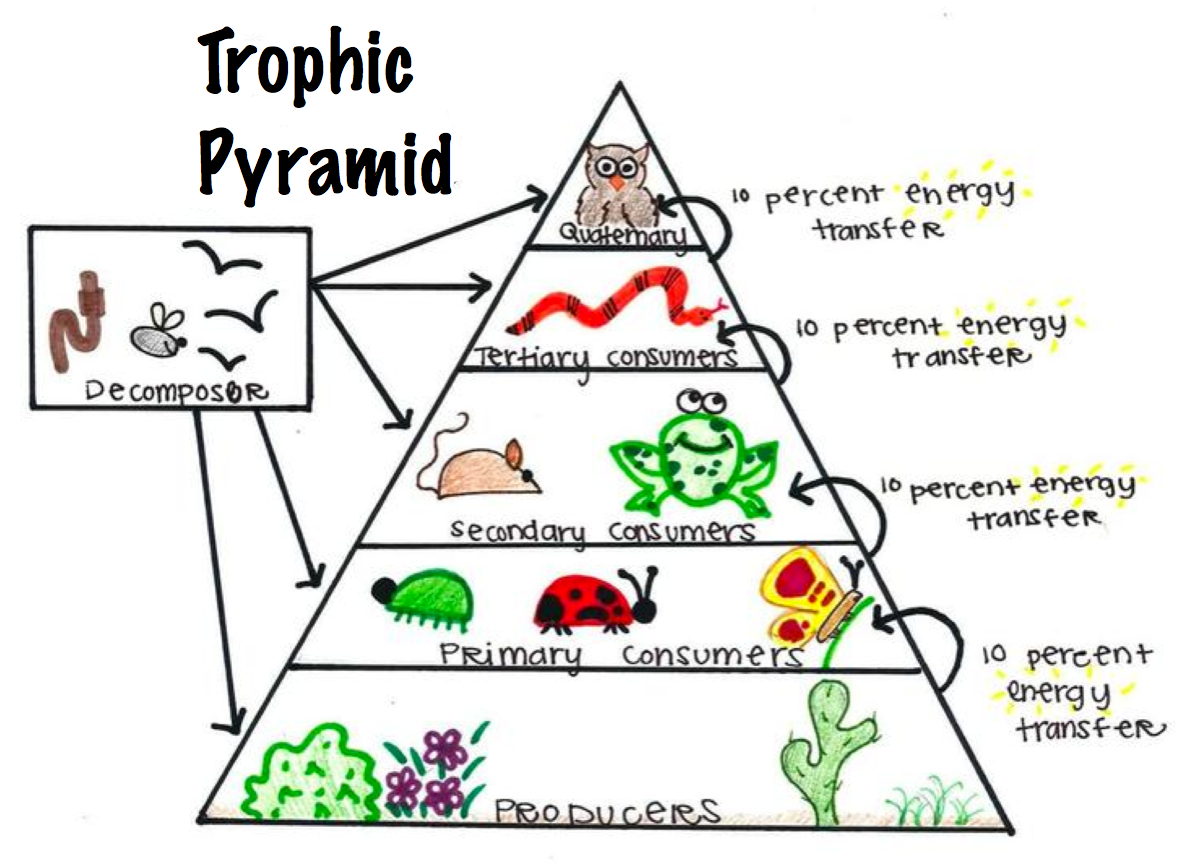
Food Chains, Food Webs, and Energy Pyramids Biology Diagrams
Trophic pyramid, the basic structure of interaction in all biological communities characterized by the manner in which food energy is passed from one trophic level to the next along the food chain starting with autotrophs, the ecosystem's primary producers, and ending with heterotrophs, the ecosystem's consumers. Food Chain and Energy pyramid is different. Food chain refers to the chain of consumption of the organisms in the ecosystem and the overall contribution of this consumption to the ecosystem. For instance, the plant gets consumed by the herbivores or omnivores, e.g. like rabbit, then the rabbit gets preyed on by the snake, the snake got consumed by the hawk, then the hawk dies, worms and
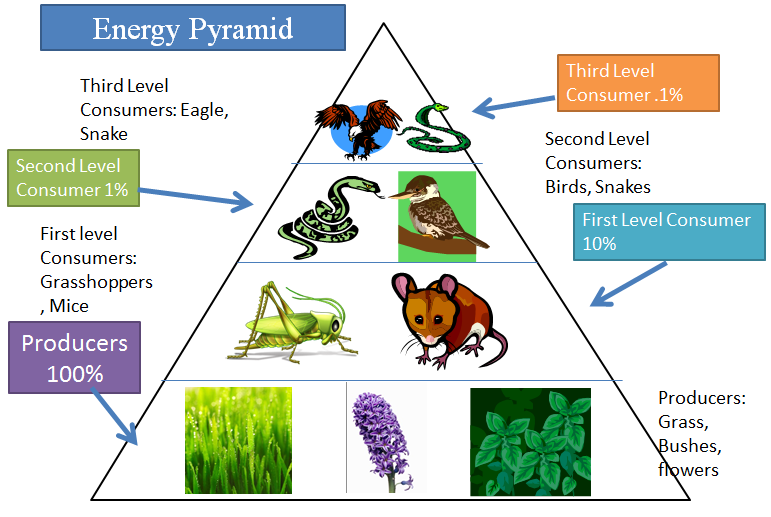
Moreover, in a food chain, the energy flow follows the 10 percent law. According to this law, only 10 percent of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the other; rest is lost into the atmosphere. This is clearly explained in the following figure and is represented as an energy pyramid. Trophic level. An energy pyramid illustrates the flow of energy through different trophic levels in an ecosystem. It shows how energy decreases as it moves up the food chain, with each level supporting the one above. The higher the trophic level, the less energy it retains. Definition. An energy pyramid is a graphical representation of the energy flow in an