The Nervous System Biology Diagrams The thalamus is ideally situated at the core of the diencephalon, Inferiorly: hypothalamus, cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum: Nuclei: Ventral group - anterior, lateral, posterior medial, All content published on Kenhub is reviewed by medical and anatomy experts. The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed The thalamic radiations are the fiber bundles that emerge from the lateral surface of the thalamus and terminate in the cerebral cortex. The external medullary lamina is a layer of myelinated fibers on the lateral surface of the thalamus close to the internal capsule. The internal medullary lamina is a thin vertical sheet of white matter that bifurcates in its anterior portion and divides the
Landmarks defining the regions of the hypothalamus include the lamina terminalis, pituitary gland, mammillary bodies, and superior hypothalamic sulcus (see Figure. The Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis). The hypothalamus is a bilateral collection of nuclei divided into 3 zones surrounding the third ventricle and the mammillary bodies. The nuclei in the periventricular zone generally regulate Your hypothalamus is connected to and communicates with your anterior lobe through a network of blood vessels. It communicates with your posterior lobe by tissue called the pituitary stalk. Your hypothalamus sends signals in the form of releasing hormones to tell the anterior and posterior pituitary when to release (secrete) its hormones.
Neuroanatomy, Hypothalamus Biology Diagrams
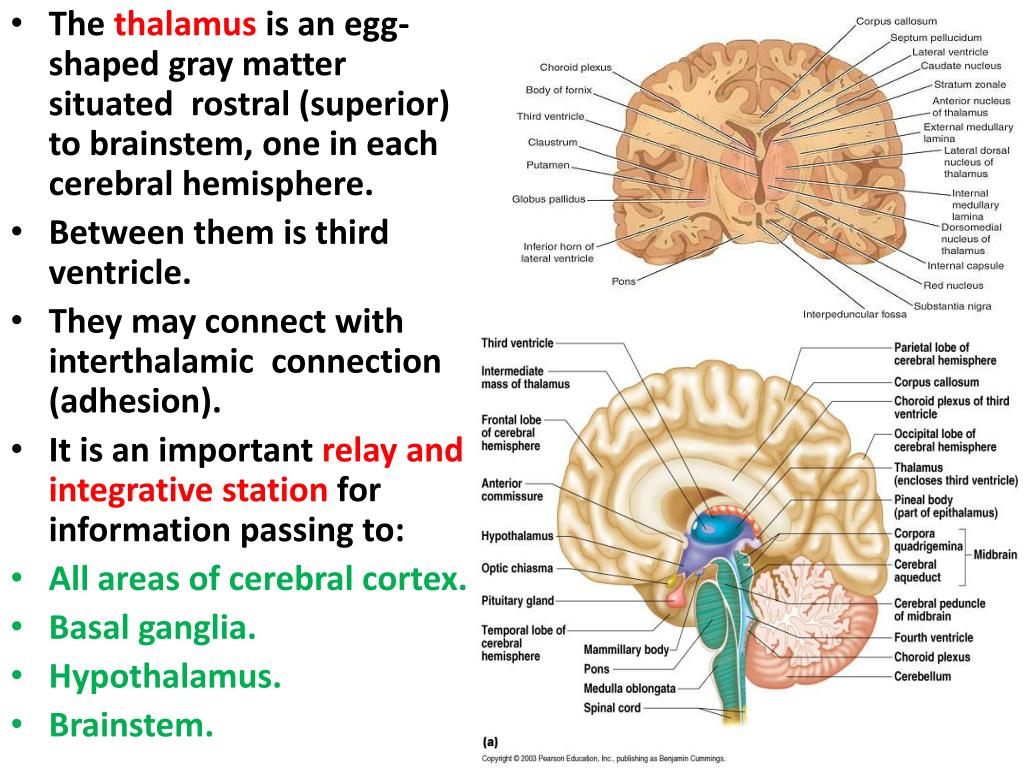
The hypothalamus is a paired structure that forms part of the diencephalon.It sits below the hypothalamic sulcus within the medial wall of the third ventricle, which separates the hypothalamus from the thalamus above. The hypothalamus is composed of several groups of nuclei which contain neurons that respond to either neural input from widespread regions of the nervous system or non-neural The document discusses the thalamus and hypothalamus. It provides details on the anatomy, internal structure, nuclei, connections and blood supply of the thalamus. It describes the relations, boundaries, nuclei and connections of the hypothalamus. The thalamus acts as a relay station and integrative center for sensory information to the cortex. The diencephalon is composed primarily of the thalamus, hypothalamus and epithalamus, which together define the walls of the third ventricle. The thalami are two elongated, ovoid structures on either side of the midline that make contact in the middle. Anatomy & Physiology. Authored by: OpenStax College. Provided by: Rice University.

Your thalamus is a central relay station for receiving incoming sensory and motor information. Your thalamus then sends this information to other parts of your brain. So, damage to your thalamus can affect many functions. Symptoms of damage to your thalamus include: Memory loss . Lack of interest or enthusiasm (apathy).
